Natural polysaccharide E414: scientific properties and European regulatory compliance
Great news: acacia gum is generally recognized as safe (GRAS).
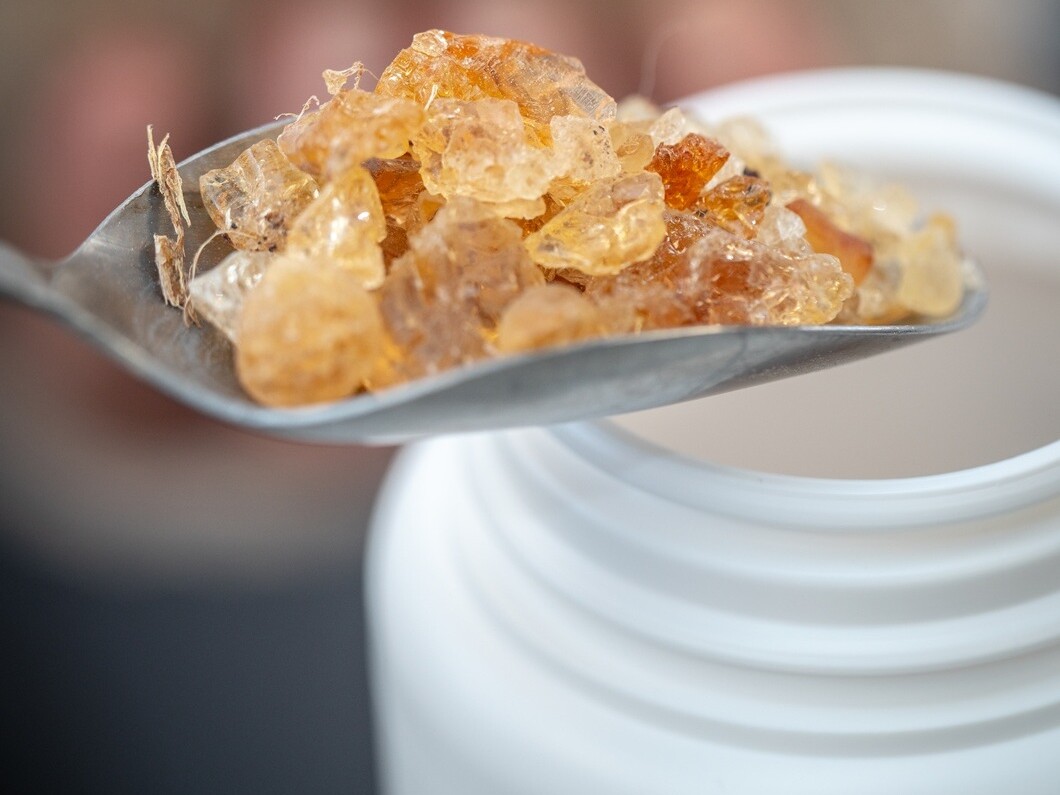
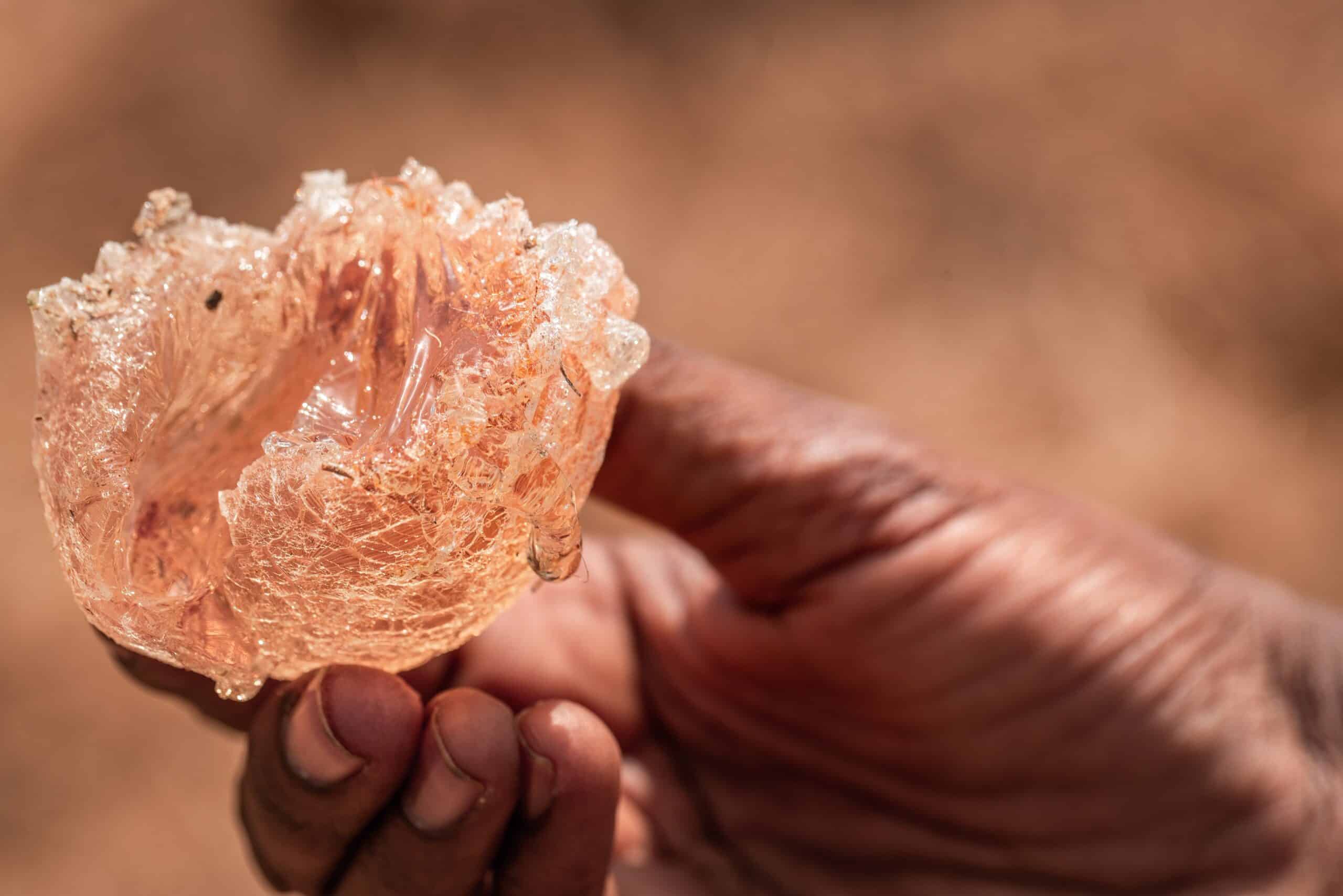
Acacia gum is a vegetal hydrocolloid that comes from acacia trees. It is neither a tree sap nor a resin, it is a tree exudate.

A scientific definition
Chemically, acacia gum is a complex non starch polysaccharide with a small fraction of protein. It is composed of polysaccharides together with calcium, magnesium and potassium. It is therefore a chain of sugars. Although its molecular conformation may vary according to botanical variety, the age of the tree concerned, and climatic conditions, its functional properties are extraordinarily constant.
Reglementation
According to the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the JECFA (joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives), there are no safety concerns in relation to acacia gum, and E414 doesn’t require a numerical ADI (acceptable daily intake).
Acacia gum is universally recognised as safe and has been scientifically proven to have no negative impact on health.
Why is acacia gum sometimes labelled as E414?
The European “E” nomenclature applies to food additives which are substances intentionally added to formulations to perform certain specific technological functions (coloring, preservation, texture, stability).
They have been tested and approved by the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and are considered safe. Acacia gum is referred to as E414 in the EFSA additive referential.
This nomenclature does not designate non-natural substances, chemically transformed or dangerous to health.